1.概念
1.链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域data,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域 next。最后一个结点的next为空。(怪我自己描述不了,就把百度百科的拿来了)
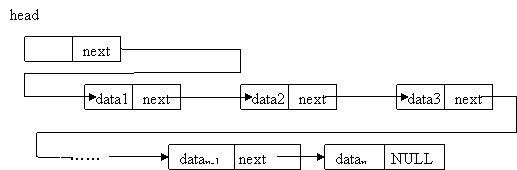 在用程序实现时,除了第一个结点以外,链表中的其他结点都可以通过前一个结点的指针域(存储了下一个结点地址)来定位,但我们该如何寻找链表的第一个结点呢?我们需要建立一个头指针来指向链表的第一个结点,这样我们就能通过头指针寻找到链表中的所有结点并进行操作。
在用程序实现时,除了第一个结点以外,链表中的其他结点都可以通过前一个结点的指针域(存储了下一个结点地址)来定位,但我们该如何寻找链表的第一个结点呢?我们需要建立一个头指针来指向链表的第一个结点,这样我们就能通过头指针寻找到链表中的所有结点并进行操作。
2.双向循环链表
双向循环链表即在单链表(上文描述的链表为单链表)的基础上进行改进,每个结点不光有存储下一个结点地址的指针域 next,还增加了存储上一个结点地址的指针域 prev,其中头(第一个结点)的 prev 指向尾结点(最后一个结点),尾结点的 next 指向头结点。

2.实现
在操作时创建 temp 指针指向链表中各元素,更改 prev 及 next 指向的结点就可以实现对链表的基本增删查改等操作。
1. list.h
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *next, *prev;
Node(int x) : data(x), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {};
};
class List
{
private:
Node *head;
int length;
public:
List();
bool list_insert(int x, int pos); //插入元素x到指定位置pos
int list_search(int x); //查找元素x,返回所在位置
bool list_delete(int x); //删除元素x
int get_data(int pos); //获取指定位置的元素
bool modify_data(int x, int pos); //修改指定位置元素数据
int get_length(); //获取链表长度
void traverse(); //遍历链表
};
2. List()
由于最开始链表中还没有元素,所以在构造函数中,指定 head 指针为空指针,链表长度 length为 0 。
List::List()
{
head = nullptr;
length = 0;
}
3. list_insert()
在插入函数中如果指定待插入结点为头个结点,pos = 0,待插入结点为尾结点,pos = -1,若 pos 大于链表长度,默认插入为尾结点。 在插入结点时:
- 链表中没有结点:head 指针指向待插入结点,待插入结点的 prev 和 next 指向自身。
- 链表中有结点: 1. pos = 0:待插入结点的 prev 指向头结点的 prev 即尾结点,next 指向头结点,头结点的 prev 指向待插入结点,head 指针指向待插入结点(待插入结点变为头结点)。 2. pos = -1:待插入结点的 prev 指向头结点的 prev 即尾结点,next 指向头结点,尾结点的 next 指向待插入结点,head 的 prev 指针指向待插入结点。 3. pos为中间:移动 temp 指针到 pos,待插入结点的 prev 和 next 分别指向 temp 结点和 temp 的 next。
bool List::list_insert(int x, int pos)
{
//pos小于-1不能插入返回false
if (pos < -1)
return false;
Node * node = new Node(x);
Node * temp = head;
//链表中有结点
if (head)
{
//插入到头结点
if (pos == 0)
{
node->next = temp;
node->prev = head->prev;
temp->prev = node;
head = node;
length++;
return true;
}
if (pos >= length) pos = -1;
//插入到尾结点
if (pos == -1)
{
node->next = head;
node->prev = head->prev;
head->prev->next = node;
head->prev = node;
length++;
return true;
}
//插入到链表中间
int index = 1;
while (index < pos)
{
temp = temp->next;
index++;
}
node->next = temp->next;
node->prev = temp;
temp->next->prev = node;
temp->next = node;
length++;
return true;
}
//链表为空
head = node;
node->next = node->prev = head;
length++;
return true;
}
4. list_search()
若链表为空返回0,未找到元素返回-1。 在链表中循环移动 temp 指针,并判断 temp 指针所指向结点的数据是否同所查找元素相同,若相同返回位置(结点位置从1开始)。
int List::list_search(int x)
{
if (!head) return 0;//空
Node * temp = head;
int index = 1;
while (index <= length)
{
if (temp->data == x) return index;
temp = temp->next;
index++;
}
return -1;//未找到
}
5. list_delete()
调用list_search()查找元素所在位置,未找到返回false。 若元素存在:
- 只有一个元素:head 指向空,length - 1。
- 其他情况:temp 移至查找位置更改指针指向,其中需要判断 temp 是否是头结点或尾结点。
bool List::list_delete(int x)
{
int index = list_search(x); //查找元素位置
if (index <= 0) return false; //未找到,返回false
else
{
Node * temp = head;
//链表只有一个元素
if (length == 1)
{
head = nullptr;
length--;
return true;
}
//移动 temp 到查找位置
for (int i=1; i!=index; i++)
temp = temp->next;
//判断是否为头结点
if (temp != head)
temp->prev->next = temp->next;
else head = temp->next;
//判断是否为尾结点
if (temp->next != head)
temp->next->prev = temp->prev;
else head->prev = temp->prev;
length--;
return true;
}
}
6. get_data()
链表为空,返回0,传入 pos 超出链表范围,返回-1。 移动 temp 指针到 pos 位置,返回 temp 数据。
int List::get_data(int pos)
{
if (!head) return 0;
if (pos > length || pos < 1) return -1;
Node * temp = head;
for (int i=1; i!=pos; i++)
temp = temp->next;
return temp->data;
}
7. modify_data()
若链表为空或 pos 超出链表范围,返回 false 。 移动 temp 指针到 pos 位置,更改 temp 数据为 x 。
bool List::modify_data(int x, int pos)
{
if (!head || pos > length || pos < 1) return false;
Node * temp = head;
for (int i=1; i!=pos; i++)
temp = temp->next;
temp->data = x;
return true;
}
8. get_length()
int List::get_length()
{
return length;
}
9. traverse()
根据 length 移动 temp 并输出 temp 数据。
void List::traverse()
{
Node * temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (count < length)
{
cout << temp->data << endl;
temp = temp->next;
count++;
}
}
本博客文章仅供博主学习交流,博主才疏学浅,语言表达能力有限,对知识的理解、编写代码能力都有很多不足,希望各路大神多多包涵,多加指点。


